Alternative energy and its sources
HYDROGEN
What is
alternative energy?
For centuries, we’ve relied on fossil fuels – coal, oil, and natural gas – to generate power. Alternative energy, in contrast, is produced from sources other than fossil fuels.(1)
When you turn on the lights or heat up your home, you’re probably not thinking about the energy that makes it possible. But energy comes from many sources, each with its own benefits and challenges. In addition to the fossil fuels that power much of our world today, some exciting alternative energy sources are becoming more viable and available every day. Here are answers to some of the most common questions about these alternative energy options.
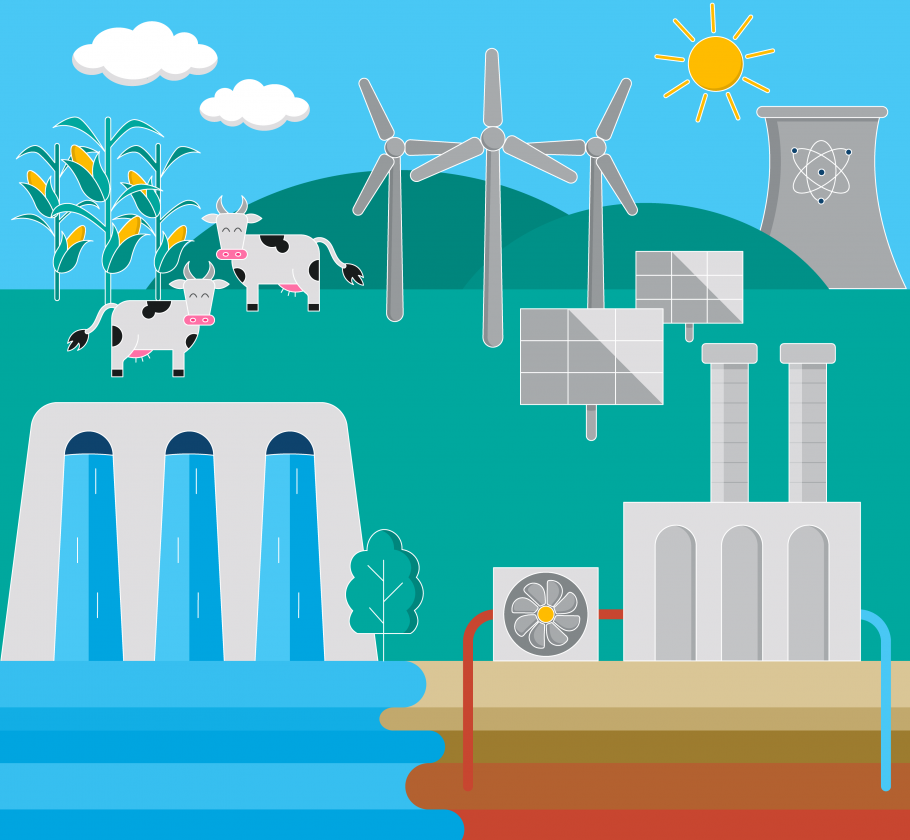

What are the main sources of alternative energy?
Alternative energy is all around us! It was used long before fossil fuels became standard sources of energy(2), and it’s returning to standard use in many traditional and innovative forms. Here are some of today’s most common sources of alternative energy:
- Bioenergy: Named from “bios,” the Greek word for “life,” bioenergy generates electricity through burning organic materials such as wood, charcoal, manure(3), and crops such as corn and soy.(4) It’s a centuries-old way to harness the sun’s chemical energy that’s stored in these sources.(5) While processing this biomass does result in greenhouse gas emissions(6), the environmental impact is lower than fossil fuels produce, and it also tends to cost less.(7)
- Geothermal: Also derived from Greek roots, this time from words meaning “earth” and “heat,” geothermal energy leverages underground reservoirs of hot water and steam to generate power.(8) The technology has been dependably delivering energy for more than a century.(9) It’s most often seen in areas with plentiful volcanos such as Iceland, where it produces more than 25 percent of the country’s electricity.(10)
- Hydropower: Moving water isn’t just powerfully beautiful – it’s also been a powerful source of energy worldwide for thousands of years.(11) Hydropower captures the energy of a controlled flow of water from a reservoir or river(12) to drive a turbine that generates electricity.(13) Nearly three-quarters of all renewable energy currently comes from hydropower.(14) The water reserves can also be used to provide water for drinking and irrigation. Though there are typically no concerns about their carbon footprint, hydropower operations can negatively affect surrounding ecosystems.(15)
- Nuclear: Everyone has heard of nuclear energy, but do you know how it’s made? Here’s the recipe. Start with an element such as uranium or thorium.(16) Split the atoms – a process called fission – to create heat and start a loop in which the process repeats. The heat produces steam, which powers a turbine to generate electricity.(17) Nuclear energy is an alternative to fossil fuels, but it’s not renewable, because there’s only so much uranium and thorium in the world, and it takes longer than a human’s lifetime to replenish it.(18) These rare elements are also difficult to access.(19)
- Solar: The sun shining on photovoltaic solar panels or radiation-concentrating mirrors makes energy to light the world.(20) Solar energy tends to be highly accessible, affordable, and environmentally friendly.(21) Indeed, in just one hour, enough solar energy reaches our planet to fulfill the world’s energy demands for a full year.(22) The biggest challenge to solar energy’s viability is that the panels need sun to work, so cloudy days, dark nights, and poor placement of the panels can hinder their ability to provide a sufficient and reliable energy supply.(23)
- Wind: In some places looking for alternative energy sources, the answer really is blowing in the wind. Turbines on land or in the water capture the kinetic energy from moving air to generate electricity.(24) Dating back at least to ancient Egypt(25), wind energy is highly efficient(26), clean, sustainable, non-polluting, easily accessible, and cost-effective.(27) Like solar energy, though, wind energy also relies on a powerful but often unreliable resource.(28)
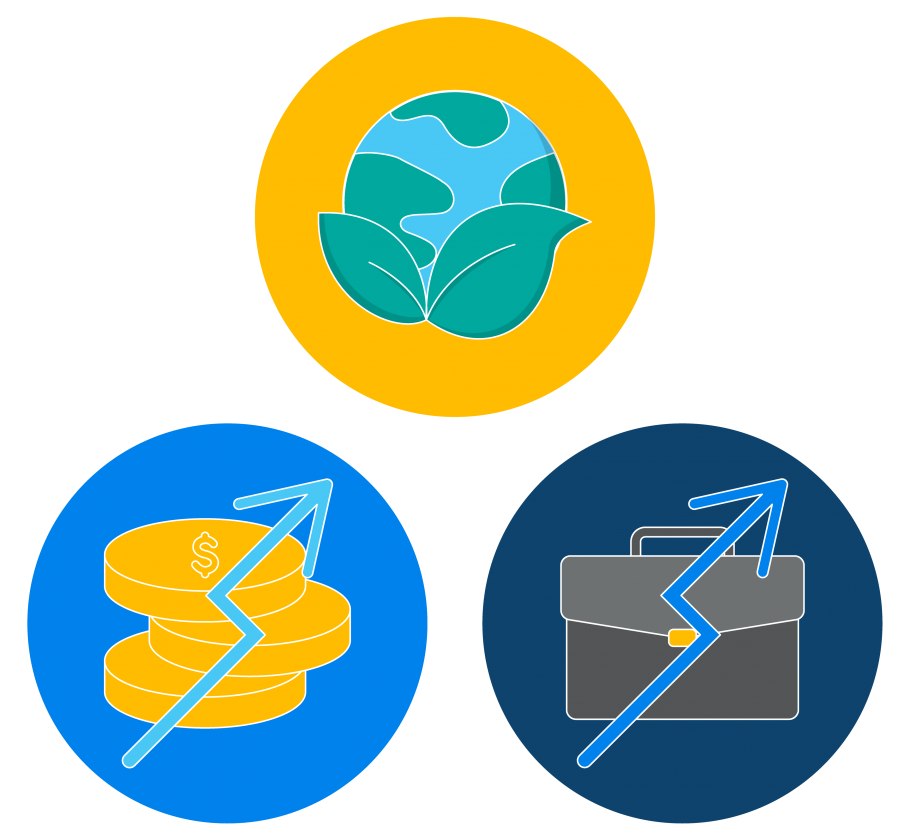

What are the main advantages of alternative energy?
Alternative energy is perhaps best known and appreciated for producing little to no carbon dioxide (CO2).(29) Its lower carbon footprint means that alternative energy does not contribute to the greenhouse effect that’s commonly associated with climate change and global warming.(30)
But wait – there’s more! Most alternative energy sources are abundant and sustainable, so they’re unlikely to disappear.(31) Using them by themselves or in conjunction with oil, gas, or coal conserves the remaining reserves of these fossil fuels.(32)
Harvesting and using alternative energy sources is also environmentally friendly.(33) The improvement in air quality could save millions of lives every year.(34)
Topping off the benefits of alternative energy, these exciting new power sources support job creation and economic development throughout the supply chain.(35)

What's the difference between alternative energy and renewable energy?
Although they may seem at first glance to be interchangeable, alternative energy and renewable energy don’t mean the same thing.
Alternative energy is a broader term, encompassing all energy sources that are not fossil fuels.(36)
Renewable energy is the sustainable subset of alternative energy. It includes sources such as the sun, wind, water, and earth that are naturally and constantly replenished, so we’ll never have to worry about exhausting them.(37)
What is the future of alternative energy?
The future looks brighter every day for alternative energy. Worldwide, the interest in alternative energy continues to rise, and government entities and private businesses are answering the call.
As demand increases, developers are gaining the experience and expertise to drive costs down.(38) As a result, incorporating alternative energy is providing solutions that are gentler not only on the environment, but also on the wallet – in some cases costing less than fossil fuels(39), and creating more jobs.(40)
So it’s perhaps no surprise that, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy sources currently comprise 26% of the world’s electricity and are expected to deliver 30% of that supply by 2024.(41) As technology to extract and deliver alternative energy keeps improving, those numbers are likely to continue to rise.(42) And the use of natural gas as a complementary energy source supports this development, making these alternative energy sources even more attractive worldwide.
